Symptoms Of Bursitis Of The Foot
Bursitis means inflammation of the bursa. A bursa is a sac-like structure that contains a lubricating fluid. A bursa is located anywhere you need a lubricating cushion-like where a muscle or tendon rubs over a bone or another muscle. Normally a bursa does its job unnoticed, but if you engage in some strenuous activity, for example, it can let you know exactly where it is. When a bursa is repeatedly irritated, the body begins to deposit calcium spicules in that location (often these deposits can be seen on X-rays). The spicules are like ground glass in the bursa, and the more you move that part of your body, the more intense the pain.
Causes
Bursitis is caused by overuse or excessive pressure on the joint, injury, infection, or an underlying condition, such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, gout, pseudogout, or ankylosing spondylitis. When bursitis is caused by an underlying condition, the condition must be treated along with the bursitis. When bursitis is caused by infection, called septic bursitis, medical treatment and antibiotics are necessary.
Symptoms
Where the tendon joins the calcaneal bone, friction can cause the spaces between the tendon, bone and skin to swell and inflame with bursitis. This constitutes a calcaneal bursa. Apart from swelling over the back of the heel, you?ll feel acute tenderness and pain when you move it or even apply light pressure. Your swollen heel may look more red than the other one, and the swelling is often so hard it can feel like bone, partly because it sometimes is, as a bony overgrowth can occur in chronic cases.
Diagnosis
Medical examination is not necessarily required in light cases where the tenderness is minimal. In all cases where smooth improvement is not experienced, medical attention should be sought as soon as possible to exclude a (partial) rupture of the Achilles tendon or rupture of the soleus muscle. This situation is best determined by use of ultrasound scanning, as a number of injuries requiring treatment can easily be overlooked during a clinical examination (Ultrasonic image). Ultrasound scanning enables an evaluation of the extent of the change in the tendon, inflammation of the tendon (tendinitis), development of cicatricial tissue (tendinosis), calcification, inflammation of the tissue surrounding the tendon (peritendinitis), inflammation of the bursa (bursitis), as well as (partial) rupture.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment consists of anti-inflammatory therapy with the use of ice, short term non steroidal therapy including ibuprofen and naproxen and selective use of cortisone injections. Cortisone injections have been shown to be a highly effective anti-inflammatory measure for relieving foot and ankle pain. Care must always be taken by the physician to insure that the injection is administered into the bursal sac and not the Achilles tendon which can cause tendon injury. Treatment also consists of the use of heel lifts or the temporary use of a shoe with a low heel. The heel lift decreases the mechanical load on the Achilles tendon. Gentle stretching of the Achilles tendon, the possible use of a splint that is worn at night as well as physical therapy as directed by your physician can be employed. Temporary activity limitations for fitness must be incorporated into the treatment plan. Any weight bearing activity for exercise that actively lifts your heel off of the ground including running, walking stair stepper will interfere with effective conservative care. Low impact activity including biking and pool tend to be safe exercises during your recovery.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is rarely done strictly for treatment of a bursitis. If any underlying cause is the reason, this may be addressed surgically. During surgery for other conditions, a bursa may be seen and removed surgically.
Contracted Second Toe
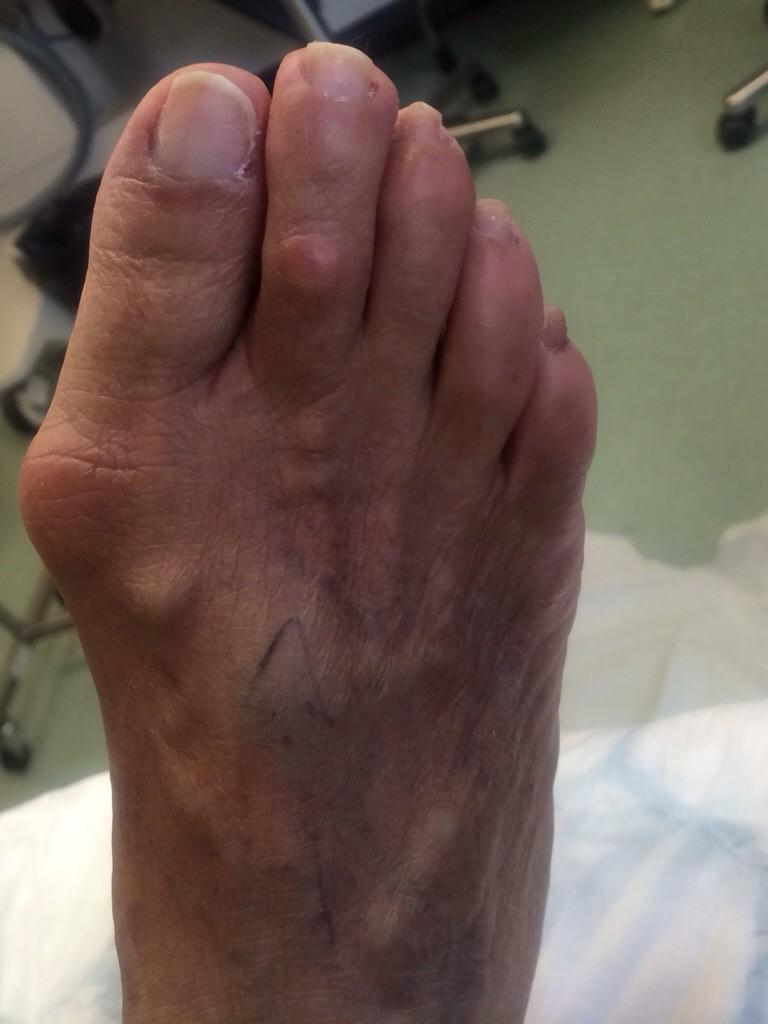
A hammertoes is a toe that tends to remain bent at the middle joint in a claw-like position. There are 2 types of hammer toe. Flexible hammer toe, can be straightened by hand. Rigid hammer toe, cannot be pulled straight and can be extremely painful. The position of the toe can also lead to corns or calluses. These may also be painful. Hammer toe may be present at birth or develop later in life due to tendons that have tightened, causing the toe's joints to curl downward. Occasionally, all toes may be bent. This may be due to problems with the peripheral nerves or the spinal cord.
Causes
Your toe contains two joints that allow it to bend at the middle and bottom. A hammertoe occurs when the middle joint becomes dislocated. Common causes of this joint dislocation include a toe injury, arthritis, a high foot arch, wearing shoes that don?t fit properly, tightened ligaments or tendons in the foot, pressure from a bunion (when your big toe points inward toward your second toe) Spinal cord or peripheral nerve damage may cause all of your toes to curl downward.
Here is a look at some of the symptoms hammertoe can cause. They include hammer-like or claw-like appearance of the toe. Pain when walking or moving the foot. Difficulty moving the toe. Corns may form on top of the toe. Callus may form on the sole of the foot. During the initial stages, you may be able to manually straighten your toe. This is called a flexible hammertoe. But as time passes, the toe will not move as easily and will continue to look like a hammer. Pressure and irritation over the joint can cause a blister to develop and become a corn over time. These corns have the potential to become infected and cause additional symptoms such as redness, bleeding, and difficulty wearing shoes and socks. Corns are the main cause of pain when hammertoes are developing.
Diagnosis
Although hammertoes are readily apparent, to arrive at a diagnosis the foot and ankle surgeon will obtain a thorough history of your symptoms and examine your foot. During the physical examination, the doctor may attempt to reproduce your symptoms by manipulating your foot and will study the contractures of the toes. In addition, the foot and ankle surgeon may take x-rays to determine the degree of the deformities and assess any changes that may have occurred.
Non Surgical Treatment
Wearing proper footwear may ease your foot pain. Low-heeled shoes with a deep toe box and flexible material covering the toes may help. Make sure there's a half-inch of space between your longest toe and the inside tip of your shoe. Allowing adequate space for your toes will help relieve pressure and pain. Avoid over-the-counter corn-removal products, many of which contain acid that can cause severe skin irritation. It's also risky to try shaving or cutting an unsightly corn off your toe. Foot wounds can easily get infected, and foot infections are often difficult to treat, especially if you have diabetes or poor circulation.
Surgical Treatment
If conservative treatments don't help, your doctor may recommend surgery to hammertoes release the tendon that's preventing your toe from lying flat. In some cases, your doctor might also remove some pieces of bone to straighten your toe.
 Prevention
Prevention
The best first step you can take is to evaluate your shoe choices. Ditch any shoes that aren?t serving your feet well. Shoes that crowd the front of your foot, especially around your toes, aggravate the existing condition and can also cause the condition to develop. If you suspect the development of hammertoe, you may also try using protective pads to prevent irritation and the development of corns. Custom orthotics to correct muscle imbalances in your feet may also help prevent hammertoe.
What Can Be Done For Hammer Toe Pain Relief
 Overview
Overview
hammertoe (hammertoe) is a deformity of the second, third, or fourth toes. In this condition, the toe is bent at the middle joint, into an upward position, causing it to resemble a hammer (sometimes decribed as ?curled toes?). Left untreated, hammer toes can become inflexible and require surgery. Toes which take Hammer toes on a curled appearance are hammer toes. Mallet toe is a similar condition, but affects the upper joint of a toe.
Causes
Your toe contains two joints that allow it to bend at the middle and bottom. A hammertoe occurs when the middle joint becomes dislocated. Common causes of this joint dislocation include a toe injury, arthritis, a high foot arch, wearing shoes that don?t fit properly, tightened ligaments or tendons in the foot, pressure from a bunion (when your big toe points inward toward your second toe) Spinal cord or peripheral nerve damage may cause all of your toes to curl downward.
 Symptoms
Symptoms
A toe stuck in an upside-down "V" is probably a hammertoe. Some symptoms are, pain at the top of the bent toe when putting on a shoe. Corns forming on the top of the toe joint. The toe joint swelling and taking on an angry red colour. Difficulty in moving the toe joint and pain when you try to so. Pain on the ball of the foot under the bent toe. Seek medical advice if your feet regularly hurt, you should see a doctor or podiatrist. If you have a hammertoe, you probably need medical attention. Ask your doctor for a referral to a podiatrist or foot surgeon. Act now, before the problem gets worse.
Diagnosis
The exam may reveal a toe in which the near bone of the toe (proximal phalanx) is angled upward and the middle bone of the toe points in the opposite direction (plantar flexed). Toes may appear crooked or rotated. The involved joint may be painful when moved, or stiff. There may be areas of thickened skin (corns or calluses) on top of or between the toes, a callus may also be observed at the tip of the affected toe beneath the toenail. An attempt to passively correct the deformity will help elucidate the best treatment option as the examiner determines whether the toe is still flexible or not. It is advisable to assess palpable pulses, since their presence is associated with a good prognosis for healing after surgery. X-rays will demonstrate the contractures of the involved joints, as well as possible arthritic changes and bone enlargements (exostoses, spurs). X-rays of the involved foot are usually performed in a weight-bearing position.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treating hammertoe involves straightening the toe, making tendons in the toes flexible again, and preventing the problem from returning. Some simple treatments include splinting the toe to keep it straight and to stretch the tendons of the foot. Using over-the-counter pads, cushions or straps to decrease discomfort Exercising the toes to relax the foot tendons (a session with a physical therapist may help you get started with foot exercises) Wearing shoes that fit properly and allow toes plenty of room to stretch out.
Surgical Treatment
In some cases, usually when the hammertoe has become more rigid and painful, or when an open sore has developed, surgery is needed. Often patients with hammertoe have bunions or other foot deformities corrected at the same time. In selecting the procedure or combination of procedures for your particular case, the foot and ankle surgeon will take into consideration the extent of your deformity, the number of toes involved, your age, your activity level, and other factors. The length of the recovery period will vary, depending on the procedure or procedures performed.
Do I Have Overpronation
Overpronation is by far the most common foot type. Pronation is not linked one-to-one with low arches. Although pronation lowers the arches, this does not mean that only those with low arches overpronate. People with high arches can also overpronate! Some of us have always overpronated, for others overpronation develops with age, weight gain, regular standing work or intensive exercise. Pronounced wear on the instep side of shoe heels can indicate overpronation, however it's best to get an accurate assessment.

Causes
Over-pronation is very prominent in people who have flexible, flat feet. The framework of the foot begins to collapse, causing the foot to flatten and adding stress to other parts of the foot. As a result, over-pronation, often leads to Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, Metatarsalgia, Post-tib Tendonitis and/or Bunions. There are many causes of flat feet. Obesity, pregnancy or repetitive pounding on a hard surface can weaken the arch leading to over-pronation. Often people with flat feet do not experience discomfort immediately, and some never suffer from any discomfort at all. However, when symptoms develop and become painful, walking becomes awkward and causes increased strain on the feet and calves.
Symptoms
Eventually, over-pronation can lead to a full list of maladies including flat feet, plantar fasciitis, plantar fibroma, neuromas, heel spurs, shin splints, ankle sprains, bunions, hammertoes, calluses, and pain in the arches, knee, hip and lower back. But it doesn?t have to go that far, because there are steps we can take to correct the over-pronation. In the vast majority of cases, we?ll prescribe custom foot orthotics, which will realign your ankles, redistribute the weight, support the arch and reduce the twisting. Many orthotics will fit snugly into your normal shoes. Although we?ll also take a look at the type of shoes you wear to see if they are contributing to the problem.
Diagnosis
One of the easiest ways to determine if you overpronate is to look at the bottom of your shoes. Overpronation causes disproportionate wear on the inner side of the shoe. Another way to tell if you might overpronate is to have someone look at the back of your legs and feet, while you are standing. The Achilles tendon runs from the calf muscle to the heel bone, and is visible at the back of the ankle. Normally it runs in a straight line down to the heel. An indication of overpronation is if the tendon is angled to the outside of the foot, and the bone on the inner ankle appears to be more prominent than the outer anklebone. There might also be a bulge visible on the inside of the foot when standing normally. A third home diagnostic test is called the ?wet test?. Wet your foot and stand on a surface that will show an imprint, such as construction paper, or a sidewalk. You overpronate if the imprint shows a complete impression of your foot (as opposed to there being a space where your arch did not touch the ground).

Non Surgical Treatment
The way a foot orthotic works is by altering the weight-bearing surface of the foot. The simulated foot improvement is only possible when standing still with full weight applied. Orthotics are of little help through most of the actual walking cycle. observationPatients may experience some symptom relief, but the orthotic cannot correct the internal osseous misalignment. Over-the-counter foot orthotics are usually of little help and wear out quickly. Custom-made foot orthotics, obtained through your doctor's office, are generally expensive. Though they last longer and have less chance of ill-effects than OTC brands, they still need to be replaced often. Over a lifetime, an individual can spend several thousands of dollars in total costs associated with orthotics and see little or no results. This is because orthotics only work when you are wearing them and do not treat the cause of the problem. In many cases, the external pressure points created by orthotics can cause more problems than solutions. Blisters, sore feet, sore joints and many other long-term complications can arise as a consequence of wearing orthotics.
Surgical Treatment
Subtalar Arthroereisis. The ankle and hindfoot bones/midfoot bones around the joint are fused, locking the bones in place and preventing all joint motion. This may also be done in combination with fusion at other joints. This is a very aggressive option usually reserved for extreme cases where no joint flexibility is present and/or the patient has severe arthritic changes in the joint.
Bunions And Running
Overview
 A bunion is an unnatural, bony hump that forms at the base of the big toe where it attaches to the foot. Often, the big toe deviates toward the other toes. When this occurs, the base of the big toe pushes outward on the first metatarsal bone, which is the bone directly behind the big toe, forming a bunion. If this happens on the little toe and fifth metatarsal, it's called a bunionette. Because a bunion occurs at a joint, where the toe bends in normal walking, your entire body weight rests on the bunion at each step. Bunions can be extremely painful. They're also vulnerable to excess pressure and friction from shoes and can lead to the development of calluses.
A bunion is an unnatural, bony hump that forms at the base of the big toe where it attaches to the foot. Often, the big toe deviates toward the other toes. When this occurs, the base of the big toe pushes outward on the first metatarsal bone, which is the bone directly behind the big toe, forming a bunion. If this happens on the little toe and fifth metatarsal, it's called a bunionette. Because a bunion occurs at a joint, where the toe bends in normal walking, your entire body weight rests on the bunion at each step. Bunions can be extremely painful. They're also vulnerable to excess pressure and friction from shoes and can lead to the development of calluses.
Causes
Some people develop bunions from wearing shoes that do not fit correctly (especially high heels or narrow-toed shoes). For other people, bunions are caused by factors beyond their control. These can include a family history of a foot type that is susceptible to bunions, neuromuscular disorders, conditions affecting the joints (e.g., arthritis), severe injury to the foot, deformities at birth, problems that affect the way a person walks (e.g., rolling in at the ankles).
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of a bunion include the base of the big toe is swollen and sticks out. The big toe is often bent towards the other toes, and sometimes the second toe is pushed to overlap the third toe. Skin around the big toe joint is red and sore. Thickened skin at the base of the big toe. Pain in the big toe or foot. Wearing shoes is painful. Pain or difficulty when walking.
Diagnosis
Your doctor can identify a bunion by examining your foot. Watching your big toe as you move it up and down will help your doctor determine if your range of motion is limited. Your doctor will also look for redness or swelling. After the physical exam, an X-ray of your foot can help your doctor identify the cause of the bunion and rate its severity.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment may be surgical or non-surgical. The goal of non-surgical treatment is to relieve pressure on the foot and to prevent pressure sores and foot ulcers. This is accomplished by prescribing accommodative shoes with a wide toe box - sandals or extra depth shoes with soft moulded insoles. It may also be possible to relax the leather on shoes to make room for a bunion. 
Surgical Treatment
The aim of surgery is to correct the cause of the bunion and prevent it growing back. Which type of surgery your podiatric surgeon recommends will depend on the severity of your bunion. Because there are risks and complications with any type of surgery, it?s not usually advised unless your bunions are causing pain, or if it is starting to deform your other toes.
What Is Severs Disease?
Sever's Disease, also known as calcaneal apophysitis, is a disease of the growth plate of the bone and is characterized by pain in the heel of a child's foot, typically brought on by some form of injury or trauma. This condition is most common in children ages 10 to 15 and is frequently seen in active soccer, football, or baseball players. Sport shoes with cleats are also known to aggravate the condition. The disease mimics Achilles tendonitis, an inflammation of the tendon attached to the back of the heel. A tight Achilles tendon contributes to Sever's Disease by pulling excessively on the growth plate of the heel bone (calcaneus). Treatment includes cutting back on sports activities, calf muscle stretching exercises, heel cushions in the shoes, icing, and/or anti-inflammatory medications.
Causes
Apart from age, other factors that may contribute to developing Sever?s disease include physical activity, any form of exercise that is weight bearing through the legs or stresses the soft tissue can exacerbate the pain of the disease, External factors, for example, running on hard surfaces or wearing inappropriate shoes during sport Overuse injury, very active children may repeatedly but subtly injure the bones, muscles and tendons of their feet and ankles. In time, the accumulated injuries cause symptoms.
Symptoms
The symptoms include pain, tenderness, swelling or redness in the heel, and they might have difficulty walking or putting pressure on the heel. If you notice that your child suddenly starts walking around on their toes because their heels hurt, that?s a dead giveaway. Kids who play sports might also complain of foot pain after a game or practice. As they grow, the muscles and tendons will catch up and eventually the pressure will subside along with the pain. But in the meantime, it can become very uncomfortable.
Diagnosis
Sever's disease is based on the symptoms reported. To confirm the diagnosis, the clinician will examine the heels and ask about the child's activity level and participation in sports. They may also squeeze the back part of the heel from both sides at the same time to see if doing so causes pain and also ask the child to stand on tiptoes to see if that position causes pain. There may be tightness in the calf muscle, which contributes to tension on the heel. Symptoms are usually worse during or after activity and get better with rest. X-rays generally are not that helpful in diagnosing Sever's disease, but they may be ordered to rule out other problems, such as fractures. Sever's disease cannot be seen on an X-ray.
Non Surgical Treatment
Occasionally, an orthotic may need to be prescribed for temporary or long-term correction of their foot biomechanics (eg flat feet or high arches). During the acute phase of Sever's disease a small heel rise or shock-absorbing heel cup placed under the heel pad of your child's foot may help to ease the symptoms. Your podiatrist or physiotherapist can assess your child's arch and guide you in the best management of your child's condition. We recommend that your child should never go barefooted during the painful stages of Sever's disease.
Exercise
Exercises that help to stretch the calf muscles and hamstrings are effective at treating Sever's disease. An exercise known as foot curling, in which the foot is pointed away from the body, then curled toward the body in order to help stretch the muscles, has also proven to be very effective at treating Sever's disease. The curling exercise should be done in sets of 10 or 20 repetitions, and repeated several times throughout the day.
What Are The Signals Of Achilles Tendon Rupture
Overview
 The Achilles tendon attaches the calf muscles in the leg to the heel bone. It is the largest yet most exposed tendon in the body. An Achilles tendon rupture injury is when the tendon fibres tear, causing symptoms of pain and loss of function. A rupture can be either partial or complete and treatment may involve surgery. Achilles tendon rupture is most common in weekend athletes trying to train too hard and is least common in well-trained professional athletes. The injury is more common in men than in women and the frequency of rupture increases over the age of 30 years.
The Achilles tendon attaches the calf muscles in the leg to the heel bone. It is the largest yet most exposed tendon in the body. An Achilles tendon rupture injury is when the tendon fibres tear, causing symptoms of pain and loss of function. A rupture can be either partial or complete and treatment may involve surgery. Achilles tendon rupture is most common in weekend athletes trying to train too hard and is least common in well-trained professional athletes. The injury is more common in men than in women and the frequency of rupture increases over the age of 30 years.
Causes
An Achilles tendon injury might be caused by several factors. Overuse. Stepping up your level of physical activity too quickly. Wearing high heels, which increases the stress on the tendon. Problems with the feet, an Achilles tendon injury can result from flat feet, also known as fallen arches or overpronation. In this condition, the impact of a step causes the arch of your foot to collapse, stretching the muscles and tendons. Muscles or tendons in the leg that are too tight. Achilles tendon injuries are common in people who participate in the following sports. Running. Gymnastics. Dance. Football. Baseball. Softball. Basketball. Tennis. Volleyball. You are more likely to tear an Achilles tendon when you start moving suddenly. For instance, a sprinter might get one at the start of a race. The abrupt tensing of the muscle can be too much for the tendon to handle. Men older than age 30 are particularly prone to Achilles tendon injuries.
Symptoms
The most common initial symptom of Achilles tendon rupture is a sudden snap at the back of the heels with intense pain. Immediately after the rupture, the majority of individuals will have difficult walking. Some individuals may have had previous complains of calf or heel pain, suggesting prior tendon inflammation or irritation. Immediately after an Achilles tendon rupture, most individuals will develop a limp. In addition, when the ankle is moved, the patient will complain of pain. In all cases, the affected ankle will have no strength. Once the Achilles tendon is ruptured, the individual will not be able to run, climb up the stairs, or stand on his toes. The ruptured Achilles tendon prevents the power from the calf muscles to move the heel. Whenever the diagnosis is missed, the recovery is often prolonged. Bruising and swelling around the calf and ankle occur. Achilles tendon rupture is frequent in elderly individuals who have a sedentary lifestyle and suddenly become active. In these individuals, the tendon is not strong and the muscles are deconditioned, making recovery more difficult. Achilles tendon rupture has been reported after injection of corticosteroids around the heel bone or attachment of the tendon. The fluoroquinolone class of antibiotics (such as ciprofloxacin [Cipro]) is also known to cause Achilles tendon weakness and rupture, especially in young children. Some individuals have had a prior tendon rupture that was managed conservatively. In such cases, recurrence of rupture is very high.
Diagnosis
During the physical exam, your doctor will inspect your lower leg for tenderness and swelling. In many cases, doctors can feel a gap in your tendon if a complete rupture has occurred. The doctor may also ask you to kneel on a chair or lie on your stomach with your feet hanging over the end of the exam table. He or she may then squeeze your calf muscle to see if your foot will automatically flex. If it doesn't, you probably have ruptured your Achilles tendon. If there's a question about the extent of your Achilles tendon injury, whether it's completely or only partially ruptured, your doctor may order a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan. This painless procedure uses radio waves and a strong magnetic field to create a computerized image of the tissues of your body.
Non Surgical Treatment
There are two treatment options available which are non-operative and operative. Non-operative treatment involves the use initially of a below-knee plaster with the foot held fully bent downwards. This usually stays in place for 2 weeks then is changed for a brace(this is a boot from the knee down to the toes with Velcro straps) which should be worn day and night. The brace will be regularly altered to allow the foot to come up to a more neutral position. The brace will be on for a further 6 weeks. After the 8 weeks you will be referred for physiotherapy to regain movement and calf strength but will probably need to wear the brace during the day for a further 4 weeks. Non-operative treatment avoids the risks of surgery but the risk of the tendon re-rupturing, which normally occurs within 3 months of discarding the brace, is 10%. 
Surgical Treatment
There are a variety of ways to repair an Achilles tendon rupture. The most common method is an open repair. This starts with an incision made on the back of the lower leg starting just above the heel bone. After the surgeon finds the two ends of the ruptured tendon, these ends are sewn together with sutures. The incision is then closed. Another repair method makes a small incision on the back of the lower leg at the site of the rupture. A series of needles with sutures attached is passed through the skin and Achilles tendon and then brought out through the small incision. The sutures are then tied together. The best surgical technique for your Achilles rupture will be determined by your orthopaedic foot and ankle surgeon.
Prevention
To prevent Achilles tendonitis or rupture, the following tips are recommended. Avoid activities that place an enormous stress on the heel (for example, uphill running or excessive jumping). Stop all activity if there is pain at the back of the heel. If pain resumes with one particular exercise, another exercise should be selected. Wear proper shoes. Gradually strengthen calf muscles with sit-ups if prior episodes of Achilles tendonitis have occurred. Always warm up with stretching exercises before any activity. Avoid high-impact sports if prior episodes of Achilles tendon injury.